


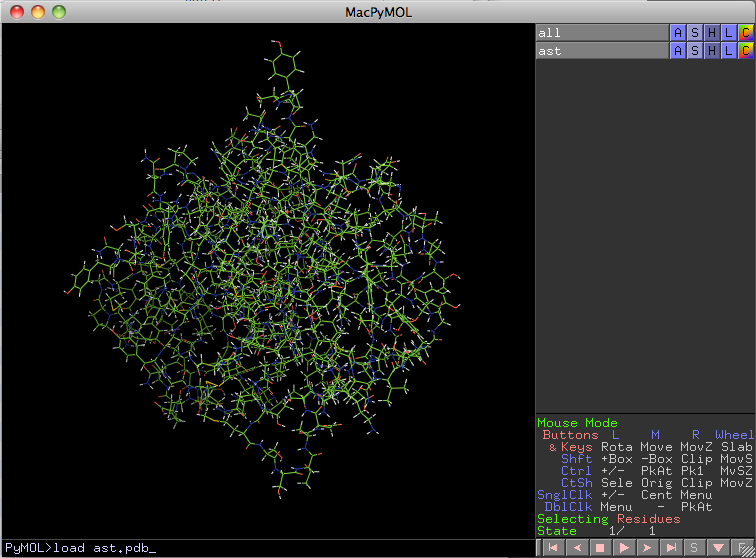
1. Open pymol and load a PDB structure. My structure is called ast.pdb.
PyMol> load ast.pdb
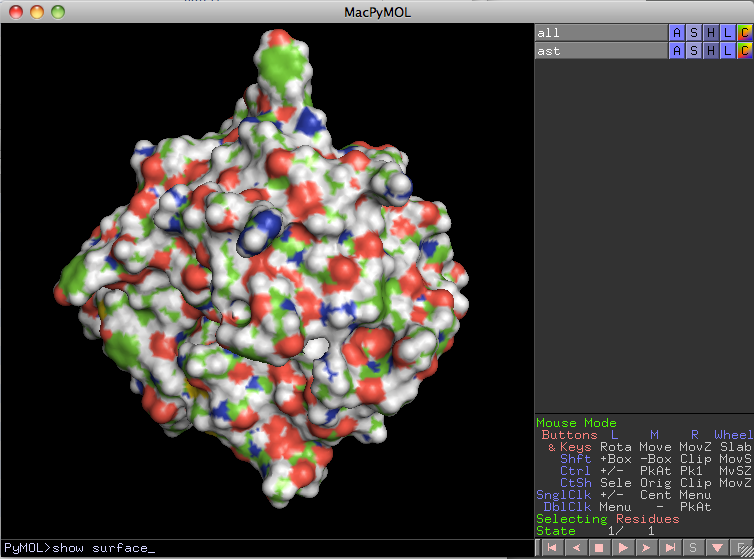
2. Display the surface (in this case for the entire structure).
PyMol> show surface
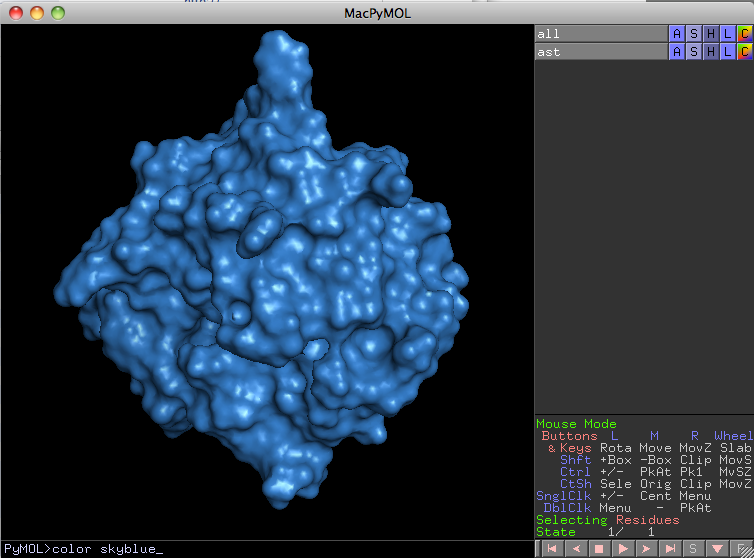
3. Surfaces look (in my opinion) much better if we add a consistent color to it. I have chosen the color skyblue.
PyMol> color skyblue
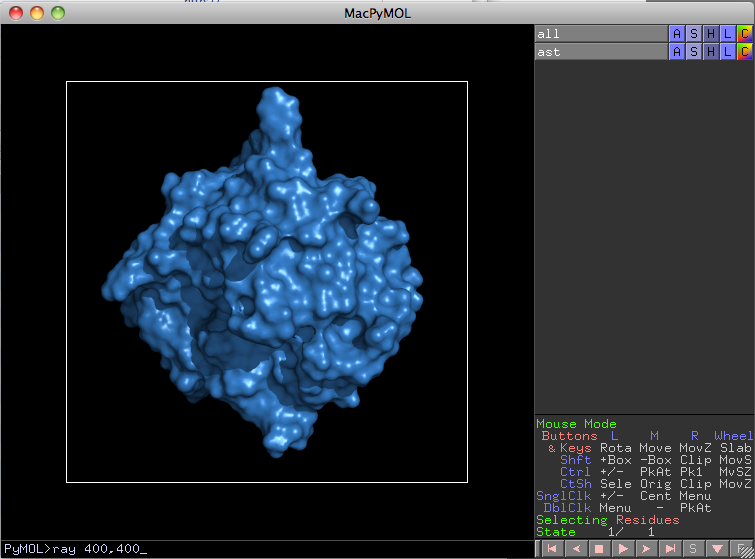
4. Ray trace the figure to give it some ligth just to check out how it looks before making the final adjustments (you can of course skip this).
PyMol> ray 400,400
5. Adjust the specular reflection to the value of 250. You will not see any effect of this before you ray trace the image, so repeat step 4 to see the result.
PyMol> set spec_power, 250
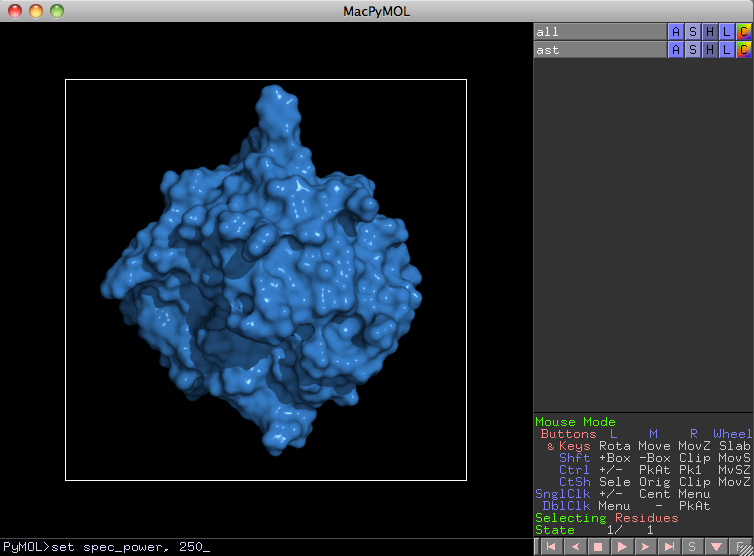
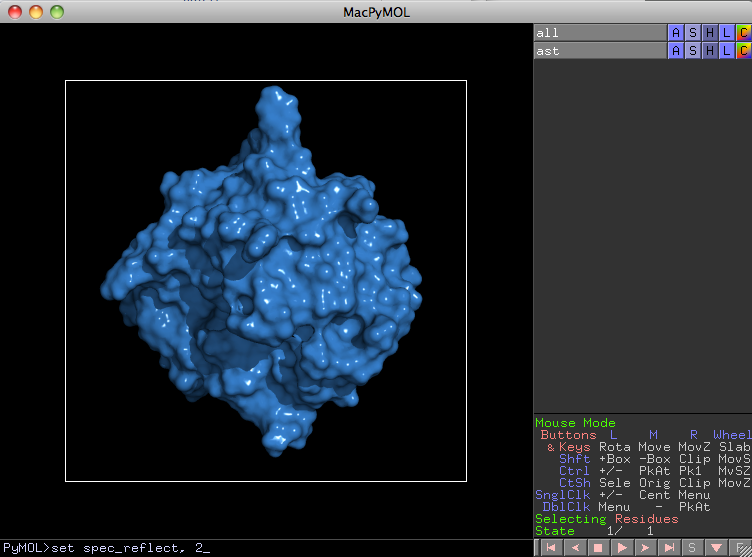
6. The final step is to adjust the specular reflection to a value of 2. This gives the glossy look that we are looking for. You will not see any effect of this before you ray trace the image, so repeat step 4 a final time.
PyMol> set spec_reflect, 2
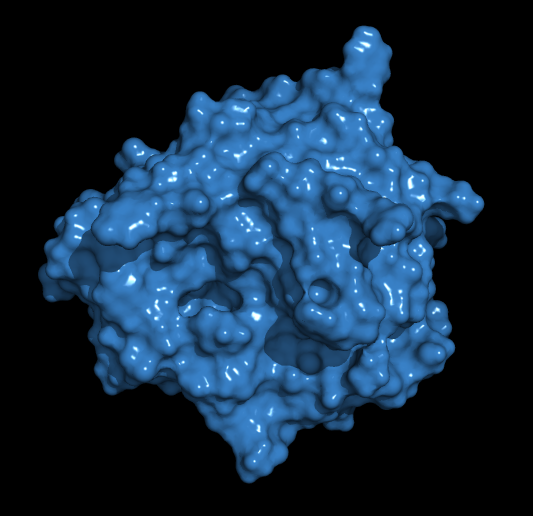
Summary:
pyMol> load structure.pdb
pyMol> show surface
pyMol> color skyblue
pyMol> set spec_power, 250
pyMol> set spec_reflect, 2
pyMol> ray xxx,yyy
Depending on your preferences, choose a different color space than the defaul RGB. Personally I prefer the CMYK color space which forces PyMOL to restrict its use of the RGB color space to a subset that can be reliably converted to CMYK using common tools such as Adobe Photoshop.
pyMol> space cmyk